A multicultural country, Vietnam is made up of 54 ethnic groups with a variety of languages. However, Vietnamese, or Tiếng Việt, remains the official language.

Dating back to the 7th century, Vietnamese is an Austroasiatic language (*) originating in northern Vietnam. It is made up of three dialects, corresponding to the three main regions of Vietnam: North, Central and South. Its vocabulary has been significantly influenced by medieval Chinese and words borrowed from French.
All three regions use the same writing system, with diagraphs (sounds) and diacritics (accents) to distinguish tones. The same word can have different meanings depending on the intonation used. Vietnamese has 6 different tones.
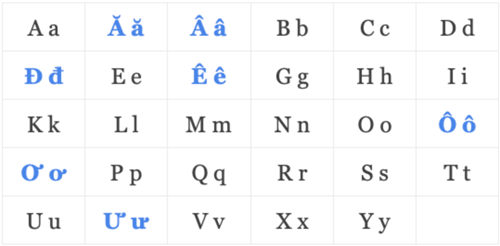
Its alphabet contains 29 letters, seven of which use four diacritics: ⟨ă⟩, ⟨â⟩, ⟨ê⟩, ⟨ô⟩, ⟨ơ⟩, ⟨ư⟩, and ⟨đ⟩. Six other diacritics are used to designate tone (⟨a⟩, ⟨à⟩, ⟨á⟩, ⟨ả⟩, ⟨ã⟩, and ⟨ạ⟩).
Note: (*) Austroasiatic languages are a family of languages spoken mainly in Southeast Asia and eastern India.








